Deep Dive Overview Update 2023
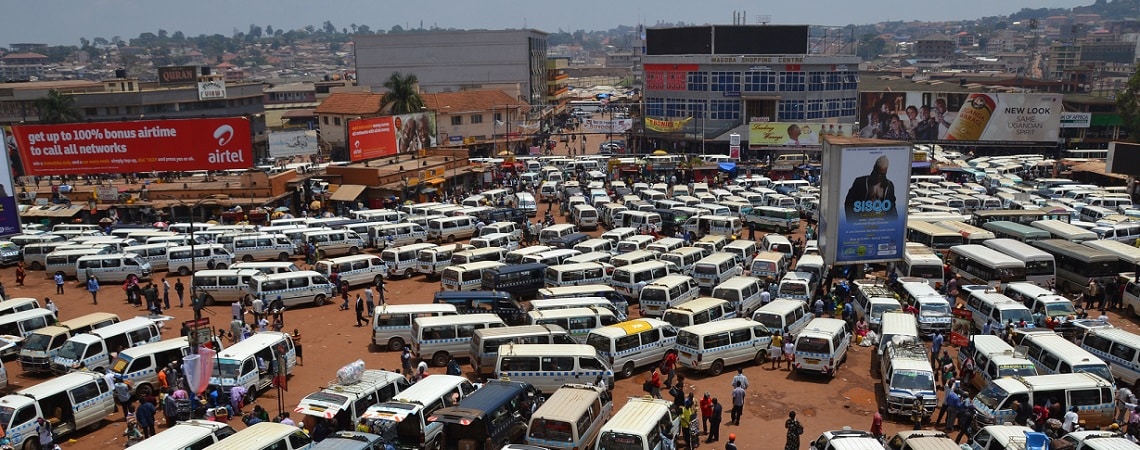
WRI Ross Center’s Deep Dive Cities Initiative focuses on locally driven strategic projects as entry points to foster long-term, cross-sectoral, and transformative change. Through the initiative, WRI provides strategic funding and additional technical capacity to support various projects, from decarbonizing transportation and enhancing climate action to strengthening disaster preparedness and urban resilience. The initiative also...